Navigate Bitcoin mining’s complex 2025 environment. Understand how network hashrate, difficulty adjustments, and hashprice interact to shape profitability. Expert analysis with actionable insights for miners facing today’s challenges.
Executive Summary: Understanding Today’s Mining Reality
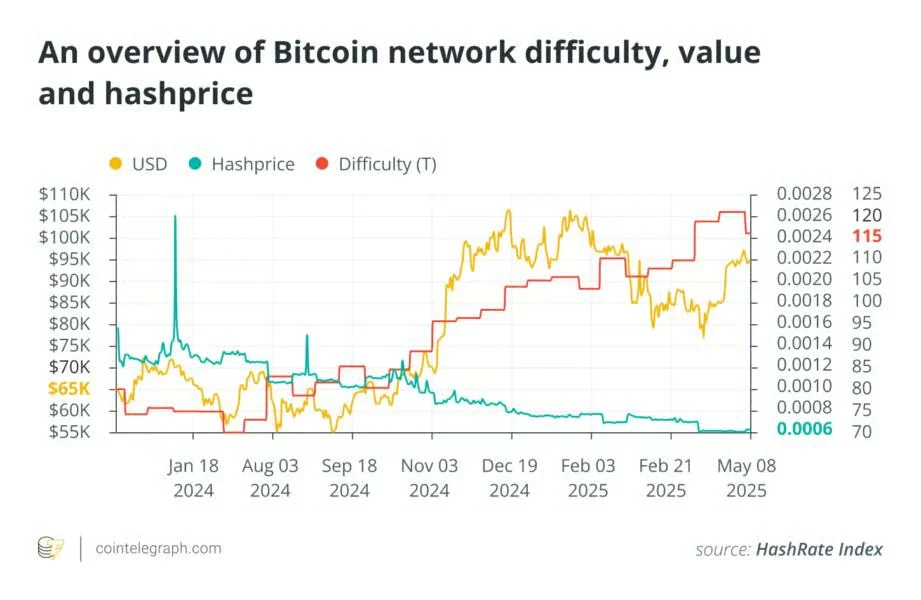
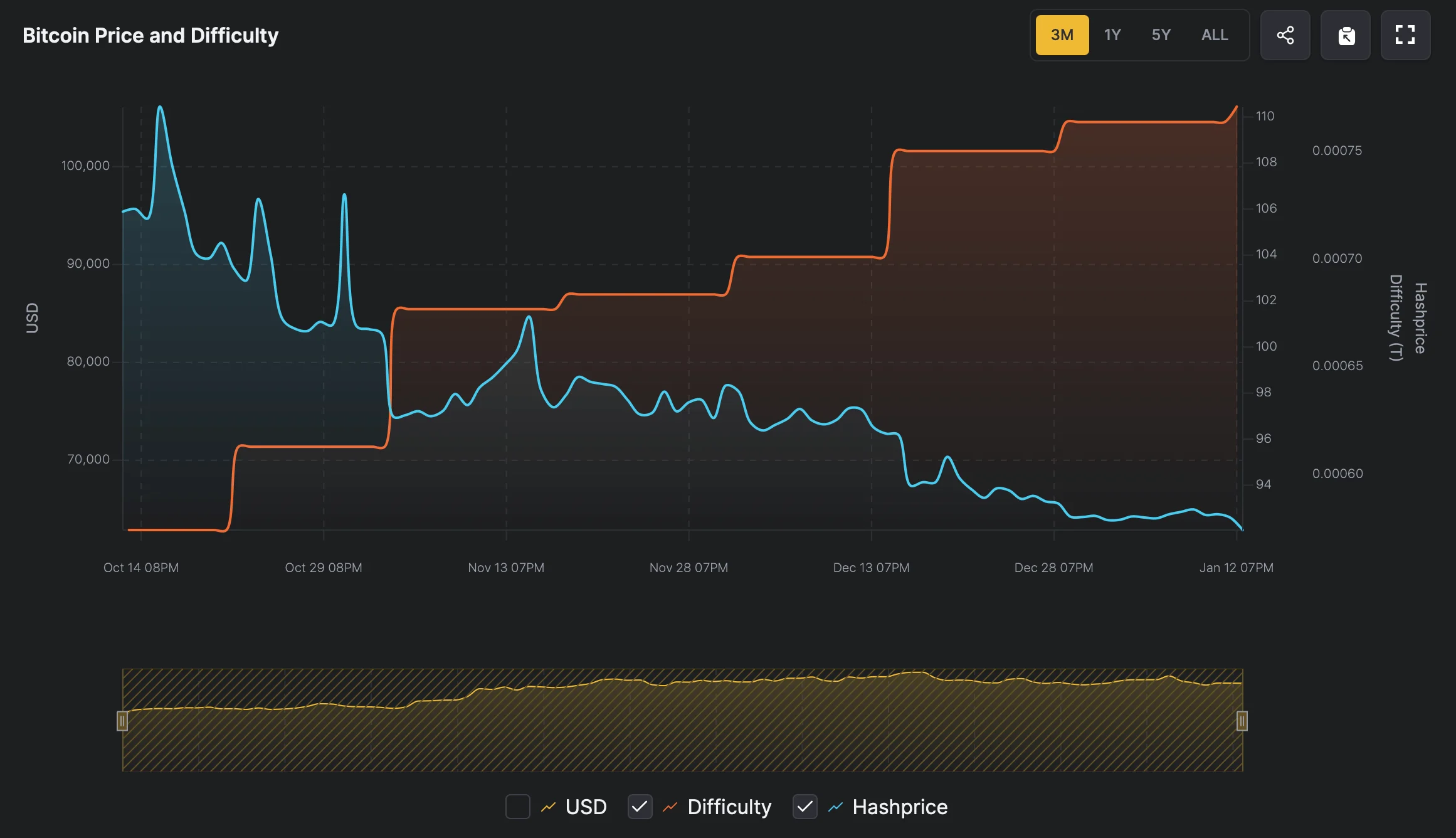
Bitcoin mining in November 2025 operates within a challenging equilibrium. With Bitcoin trading around $103,000, network hashrate exceeding 1.1 ZH/s, and difficulty at 155.97T, miners face unprecedented competition. The current hashprice of approximately $42-43 per PH/s per day sits near critical profitability thresholds, creating survival-mode conditions for many operations. This comprehensive analysis explores the intricate relationships between these three core metrics and provides strategic guidance for navigating today’s mining environment.
The Current State: November 2025 Network Metrics
Hashrate: Record Highs Despite Profitability Pressure
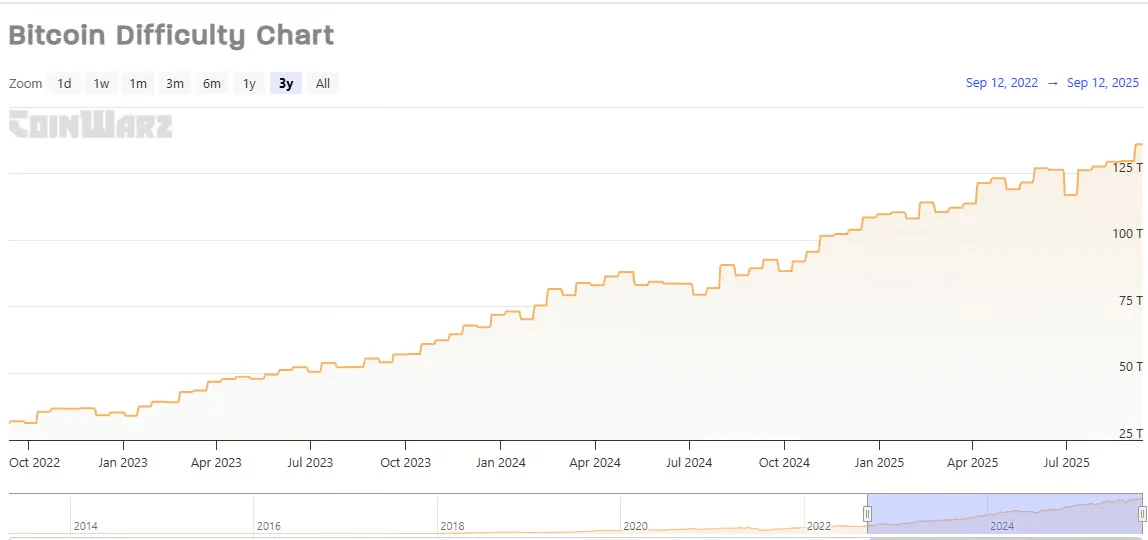
The Bitcoin network hashrate has reached historic levels, currently hovering around 1.102 ZH/s (zettahash per second). This represents continued growth in mining capacity despite compressed margins following the April 2024 halving event. The sustained hashrate increase indicates strong institutional confidence and ongoing infrastructure investments, particularly from publicly traded mining companies.
Difficulty Adjustment: Adaptive Network Security
Network difficulty stands at 155.97T, with the next adjustment estimated to decrease by 2-3% within the coming days. This metric automatically recalibrates every 2,016 blocks (approximately two weeks) to maintain the 10-minute block time target. The current difficulty level reflects the network’s robust security posture but also intensifies competition for block rewards.
Hashprice Reality: Approaching Critical Levels
Perhaps most critical for operational miners, hashprice has declined to $42-43 per PH/s daily—approaching multi-month lows not seen since early 2024. This metric directly translates network conditions into revenue per unit of hashpower, making it the most tangible profitability indicator. With electricity costs typically ranging $0.05-0.08 per kWh for competitive operations, many miners now operate on razor-thin margins.
Understanding the Three-Way Relationship
How Hashrate Drives Difficulty
Network hashrate serves as the independent variable in Bitcoin’s difficulty adjustment algorithm. When more mining equipment comes online, blocks are found faster than the target 10-minute interval. The protocol responds by increasing difficulty at the next adjustment, restoring the intended block production rate. This self-balancing mechanism ensures predictable Bitcoin issuance regardless of mining capacity.
The Hashprice Equation: Where Supply Meets Demand
Hashprice emerges from the intersection of block rewards, transaction fees, Bitcoin price, and total network hashrate. Currently calculated as: Hashprice = (Block Reward × BTC Price + Transaction Fees) ÷ Network Hashrate. With block rewards fixed at 3.125 BTC post-halving and transaction fees providing minimal contribution during low-activity periods, hashprice becomes highly sensitive to Bitcoin price fluctuations and hashrate competition.
The Competitive Spiral Effect
These three metrics create a self-reinforcing cycle. High Bitcoin prices attract more hashrate → increased hashrate triggers difficulty adjustments → rising difficulty without proportional price increases compresses hashprice → compressed margins force inefficient miners offline → reduced competition temporarily improves conditions for survivors. Understanding this cycle helps predict market dynamics and time equipment investments.
Comparison: Mining Equipment Efficiency in 2025
Table 1: Leading Bitcoin Miners Performance Analysis
| Mining Model | Hashrate | Power Consumption | Efficiency (J/TH) | Est. Daily Revenue* | Break-even Power Cost** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bitmain S21 XP Hydro | 473 TH/s | 5,360W | 11.3 J/TH | $19.85 | $0.154/kWh |
| Bitmain Antminer S21+ | 234 TH/s | 3,510W | 15.0 J/TH | $9.82 | $0.116/kWh |
| Bitmain Antminer S21 | 200 TH/s | 3,500W | 17.5 J/TH | $8.40 | $0.100/kWh |
| MicroBT M66S++ | 356 TH/s | 5,518W | 15.5 J/TH | $14.95 | $0.112/kWh |
| MicroBT M60S | 176 TH/s | 3,348W | 19.0 J/TH | $7.39 | $0.092/kWh |
| Canaan Avalon A1566I | 185 TH/s | 3,420W | 18.5 J/TH | $7.77 | $0.094/kWh |
*Based on hashprice of $42/PH/s **Assuming all revenue consumed by electricity at this rate
Source: Industry data compiled November 2025
Efficiency Gap: The New Competitive Advantage
The data reveals a critical truth: efficiency gaps of just 3-5 J/TH can determine survival in current market conditions. Hydro-cooled flagship models like the S21 XP operate at break-even power costs 50% higher than older generation equipment, providing substantial operational flexibility. For miners paying above $0.10/kWh, only the most efficient equipment remains viable at current hashprice levels.
The Upgrade Calculus: When to Refresh Hardware
Equipment decisions now require careful financial modeling. A Bitmain S21 series miner priced at approximately $3,500-5,000 generates $8-10 daily at current rates, suggesting a 500-600 day payback period before considering electricity costs. However, miners must also factor potential Bitcoin price appreciation, difficulty increases, and the compounding effect of delayed upgrades on competitive positioning.
Post-Halving Impact: The 2024 Effect on 2025 Operations
The Immediate Aftermath: Revenue Halving Reality
The April 2024 halving reduced block rewards from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC, instantly cutting miner revenue by 50%. While Bitcoin price appreciated from approximately $64,000 at halving to current $103,000 levels, this 61% increase hasn’t fully compensated for reward reduction when accounting for concurrent hashrate growth from 600 EH/s to 1,100 EH/s (83% increase).
Industry Consolidation: Survival of the Efficient
The halving accelerated industry consolidation. Smaller operations with higher electricity costs or outdated equipment faced immediate pressure. Publicly traded miners with access to capital markets expanded capacity, while many private operators either upgraded equipment, secured cheaper power contracts, or exited entirely. This “efficiency Darwinism” continues shaping the competitive landscape.
Transaction Fee Dependency: The Missing Revenue Stream
Unlike previous market cycles, transaction fees haven’t provided meaningful relief. During 2024’s ordinals inscription boom, fees briefly contributed 10-20% of mining revenue, but current baseline conditions see fees representing only 2-5% of block rewards. This makes miners almost entirely dependent on Bitcoin price appreciation to maintain profitability against rising hashrate competition.
Strategic Mining Scenarios: Q4 2025 Outlook
Table 2: Scenario Analysis – December 2025 Projections
| Scenario | BTC Price | Network Hashrate | Difficulty | Hashprice | Market Sentiment | Probability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bear Case | $85,000-95,000 | 1,200-1,250 ZH/s | 165-172T | $32-37/PH/s | Miner capitulation accelerates | 25% |
| Base Case | $95,000-110,000 | 1,100-1,200 ZH/s | 155-165T | $40-48/PH/s | Stable consolidation continues | 50% |
| Bull Case | $110,000-130,000 | 1,050-1,150 ZH/s | 148-160T | $50-62/PH/s | Price rally revives margins | 20% |
| Breakthrough | $130,000+ | 1,000-1,100 ZH/s | 140-155T | $65-80/PH/s | New cycle high triggers expansion | 5% |
Projections based on current network conditions and historical correlation patterns
Reading the Signals: What Drives Each Scenario
The bear case assumes Bitcoin price retracement to test support levels, triggering widespread miner capitulation among marginal operations. This would reduce hashrate and difficulty, eventually stabilizing conditions but causing significant industry distress. The base case projects continued current dynamics with modest improvements.
The bull case requires sustained Bitcoin price momentum driven by favorable macroeconomic conditions, ETF inflows, or geopolitical developments increasing digital asset demand. The breakthrough scenario, while lower probability, mirrors previous post-halving cycles where delayed price reactions eventually create highly favorable mining conditions.
Positioning Your Operation: Action Plans by Scenario
For bear case preparation: Prioritize efficiency upgrades, lock in long-term power contracts at favorable rates, maintain adequate cash reserves to weather 90-120 day low-profitability periods, and consider strategic equipment purchases during potential fire sales from distressed operators.
For base/bull case optimization: Focus on gradual capacity expansion using proven efficient equipment, diversify revenue streams through emerging opportunities like AI compute integration, and maintain operational flexibility to scale with improving conditions.
Cost Management: The Profitability Equation
Electricity: The Dominant Variable
Electricity represents 60-75% of operational costs for most mining operations at current hashprice levels. A facility paying $0.06/kWh versus $0.09/kWh enjoys 50% better margins on identical equipment—often the difference between profit and loss. Geographic arbitrage, renewable energy integration, and strategic power agreements define competitive positioning.
Infrastructure and Cooling: The Hidden Costs
Beyond raw power costs, infrastructure investments significantly impact total cost of ownership. Traditional air-cooled facilities require extensive HVAC systems consuming 15-20% additional power. Modern hydro-cooling solutions reduce cooling overhead to 5-8% while enabling higher density deployments and extending equipment lifespan through lower operating temperatures.
Operational Efficiency: Minimizing Downtime
Mining revenue accrues 24/7, making uptime critical. A well-managed operation achieves 98-99% uptime, while poorly maintained facilities may see 90-95%—a 4-8% revenue differential. Proactive maintenance, redundant power systems, remote monitoring infrastructure, and experienced technical staff justify their costs through maximized production.
Equipment Selection Guide: 2025 Recommendations
Flagship Performance: For Low-Cost Power Environments
Operations with access to electricity below $0.05/kWh can justify premium efficiency equipment. The Bitmain S21 XP Hydro and similar flagship models provide maximum hashrate density and efficiency, optimizing revenue per square foot of facility space. These investments make sense for long-term strategic positioning despite higher upfront costs around $8,000-12,000 per unit.
Balanced Approach: Mainstream Efficiency Models
For most operations with power costs in the $0.05-0.07/kWh range, models like the Bitmain S21+ or S21 standard represent optimal value. These miners offer strong efficiency at 15-17.5 J/TH with more accessible pricing around $3,500-5,500. Their balance of performance, cost, and availability makes them the workhorses of 2025 mining operations.
Value Segment: Selective Opportunities
Older generation efficient equipment like S19 XP models can still provide value in specific scenarios: operations with very low power costs (<$0.04/kWh), secondary deployments using stranded energy, or capital-constrained operators accepting shorter economic lifespans. However, avoid equipment exceeding 20 J/TH efficiency unless power is essentially free.
Alternative Algorithms: Diversification Considerations
While Bitcoin remains dominant, miners might explore multi-algorithm strategies. Equipment like the Bitmain L9 for Scrypt mining (Litecoin/Dogecoin) or specialized ASIC miners for emerging networks can provide portfolio diversification, though Bitcoin typically offers superior liquidity and market depth.
Global Mining Dynamics: Geographic Considerations
North American Resilience: Infrastructure Advantages
North America, particularly the United States, dominates institutional Bitcoin mining with approximately 35-40% of global hashrate. Advantages include regulatory clarity, access to stranded natural gas and renewable energy, sophisticated capital markets for mining companies, and robust infrastructure. However, energy costs vary dramatically by region, from $0.03/kWh in West Texas to $0.08+/kWh in coastal regions.
Emerging Markets: The New Frontier
Countries like Paraguay, Ethiopia, Kazakhstan, and UAE emerge as mining destinations offering competitive electricity rates ($0.02-0.05/kWh), often from excess hydroelectric or natural gas capacity. These locations require careful evaluation of political stability, regulatory environment, infrastructure reliability, and repatriation considerations, but can provide substantial cost advantages for experienced operators.
Asia-Pacific Evolution: Post-China Landscape
Following China’s 2021 mining ban, hashrate redistributed globally. While direct mainland Chinese mining remains prohibited, nearby regions like Kazakhstan initially absorbed capacity before facing their own regulatory pressures. Currently, Southeast Asian countries show growing interest, though infrastructure limitations and regulatory uncertainty require cautious evaluation.
Risk Management: Protecting Your Operation
Price Volatility: Hedging Strategies
Bitcoin’s price volatility directly impacts mining profitability. Sophisticated operations employ hedging strategies: selling forward contracts to lock in minimum revenue floors, using options to protect downside while maintaining upside exposure, or implementing systematic selling schedules to ensure operational cash flow regardless of short-term price movements. Small operators might simply maintain 3-6 months of operational expenses in stable reserves.
Equipment Obsolescence: Technology Refresh Planning
ASIC miners depreciate rapidly as newer, more efficient models emerge. Plan for 3-4 year replacement cycles when modeling investments. Monitor efficiency trends—if new equipment achieves 20%+ efficiency improvements, older gear loses competitiveness quickly. Set aside reserves for periodic upgrades rather than facing sudden obsolescence crises.
Regulatory Evolution: Compliance Preparation
Mining regulations continue evolving globally. Stay informed about emerging requirements around energy consumption reporting, environmental impact assessments, taxation methodologies for mined Bitcoin, and local licensing requirements. Proactive compliance and engagement with regulatory bodies positions operations favorably as frameworks solidify.
Future Outlook: Beyond 2025
Next Halving: 2028 Preparation
While the 2028 halving seems distant, forward-thinking miners already consider its implications. Block rewards will reduce to 1.5625 BTC, requiring either substantially higher Bitcoin prices or dramatically improved efficiency to maintain current profitability models. Equipment purchased today should remain competitive through this next cycle, emphasizing the importance of efficiency-first purchasing decisions.
Technology Evolution: What’s Next
Mining hardware approaches physical limitations of current semiconductor technology. Future improvements may come through architectural innovations rather than pure node shrinking, specialized cooling technologies enabling higher performance, or entirely new proof-of-work algorithms (though Bitcoin’s SHA-256 shows no signs of changing). Monitor developments in 3nm and 2nm chip manufacturing for next-generation efficiency breakthroughs.
Industry Maturation: Professional Mining Era
Bitcoin mining increasingly resembles traditional infrastructure industries—capital intensive, operationally focused, with thin margins requiring scale and efficiency. The “hobbyist miner” era has largely concluded. Success requires professional approach to site selection, equipment procurement, operational management, financial planning, and risk management comparable to traditional commodity extraction industries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Is Bitcoin mining still profitable in November 2025?
Yes, but profitability highly depends on your specific conditions. With hashprice around $42-43/PH/s and Bitcoin at $103,000, mining remains viable for operations with efficient equipment (under 17 J/TH) and competitive electricity rates (below $0.07/kWh). Margins are compressed compared to previous years, requiring careful cost management and operational excellence.
Q2: What’s the minimum investment to start mining profitably?
For individual operations, expect minimum $10,000-15,000 for 2-3 modern efficient ASICs, plus infrastructure costs (power distribution, cooling, monitoring systems). However, many experts recommend $50,000+ investments to achieve sufficient scale for meaningful returns and risk diversification. Consider hosted mining solutions if capital-constrained, though this reduces control and margins.
Q3: How does the current difficulty level affect my mining rewards?
At 155.97T difficulty, your mining equipment competes with approximately 1.1 ZH/s of global hashrate for 3.125 BTC block rewards every ~10 minutes. A 200 TH/s miner represents 0.000018% of network hashrate, earning approximately $8.40 daily at current conditions. As difficulty adjusts up or down, your relative share and earnings change inversely—lower difficulty means more rewards for the same hashrate.
Q4: Should I wait for Bitcoin price increases before investing in mining equipment?
Mining equipment decisions require nuanced analysis. Waiting for price increases often means missing optimal purchasing windows when equipment is available and reasonably priced. Consider dollar-cost averaging into mining capacity, purchasing some equipment now while maintaining reserves for opportunistic additions. Equipment ordered during market weakness often delivers optimal lifetime returns as conditions improve during the operational period.
Q5: What’s the current payback period for mining equipment?
At current conditions, expect 500-700 day gross payback periods for efficient equipment before electricity costs, or 800-1,200+ days for full profitability accounting for all expenses. However, these calculations assume static conditions. Bitcoin price appreciation, efficiency advantages over aging network equipment, and potential hashrate reductions from miner capitulation can dramatically improve actual returns. Model multiple scenarios rather than relying on single-point calculations.
Q6: How do I choose between air-cooled and hydro-cooled miners?
Air-cooled miners like the standard S21 series offer lower upfront costs and simpler infrastructure requirements, suitable for smaller operations or moderate climates. Hydro-cooled models require specialized infrastructure (heat exchangers, coolant distribution) but enable higher density deployments, lower cooling costs, quieter operation, and extended equipment lifespan. Choose hydro for large-scale professional operations with >100 units; air-cooling remains practical for smaller deployments.
Q7: What’s the impact of transaction fees on mining profitability?
Currently, transaction fees contribute only 2-5% of mining revenue during typical network activity. During high-congestion periods (like the 2024 ordinals boom), fees temporarily spiked to 15-25% of rewards, significantly boosting profitability. However, base your financial models on block rewards alone, treating fee revenue as bonus upside rather than dependable income. Future Bitcoin adoption could increase baseline fee contributions, though this remains speculative.
Q8: How often should I upgrade my mining equipment?
Plan for 3-4 year equipment refresh cycles when purchasing. Monitor efficiency trends—if new generations achieve 15-20%+ improvements while your equipment approaches 18-20 J/TH efficiency, prioritize upgrades. Also consider opportunity costs: selling current equipment while it retains residual value to fund newer models often provides better returns than operating older equipment until complete obsolescence. Maintain rolling upgrade schedules rather than full-fleet replacements.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complex Mining Triangle
The relationship between hashrate, difficulty, and hashprice creates a dynamic, self-balancing ecosystem that rewards efficiency, strategic planning, and operational excellence. November 2025’s challenging conditions—characterized by high difficulty, compressed hashprice, and intense competition—separate professional operations from marginal players.
Success requires a multi-dimensional approach: securing competitive electricity rates, investing in efficient equipment, maintaining operational excellence, implementing robust risk management, and thinking strategically about long-term positioning rather than short-term volatility.
For those considering entering or expanding mining operations, current conditions offer both challenges and opportunities. Compressed margins during consolidation phases often precede the most profitable operational periods as market conditions improve and less-efficient competitors exit. The key is surviving the squeeze with strong fundamentals intact.
Ready to optimize your mining operation? Explore our selection of current-generation efficient mining equipment, backed by direct manufacturer relationships, competitive pricing, professional transportation, and comprehensive technical support. Contact our expert team for personalized consultation on equipment selection, profitability modeling, and operational strategy tailored to your specific conditions.
The Bitcoin mining landscape continues evolving—stay informed, stay efficient, and stay competitive.